ExoMy
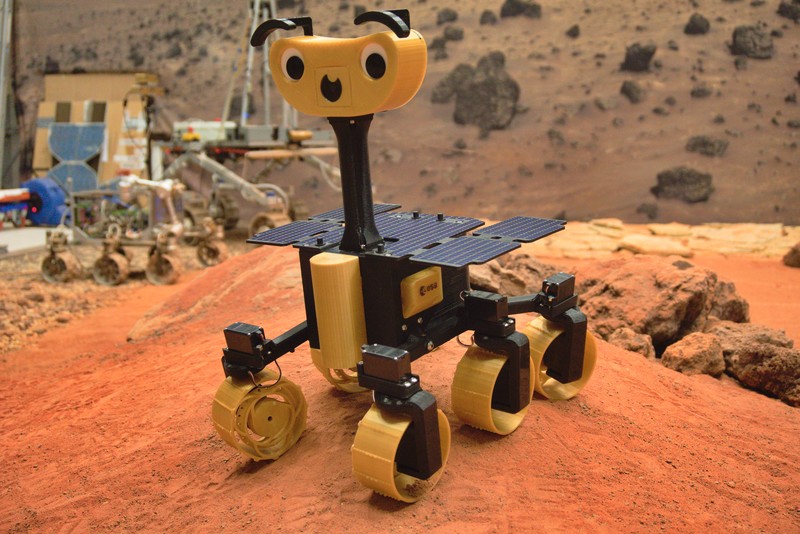


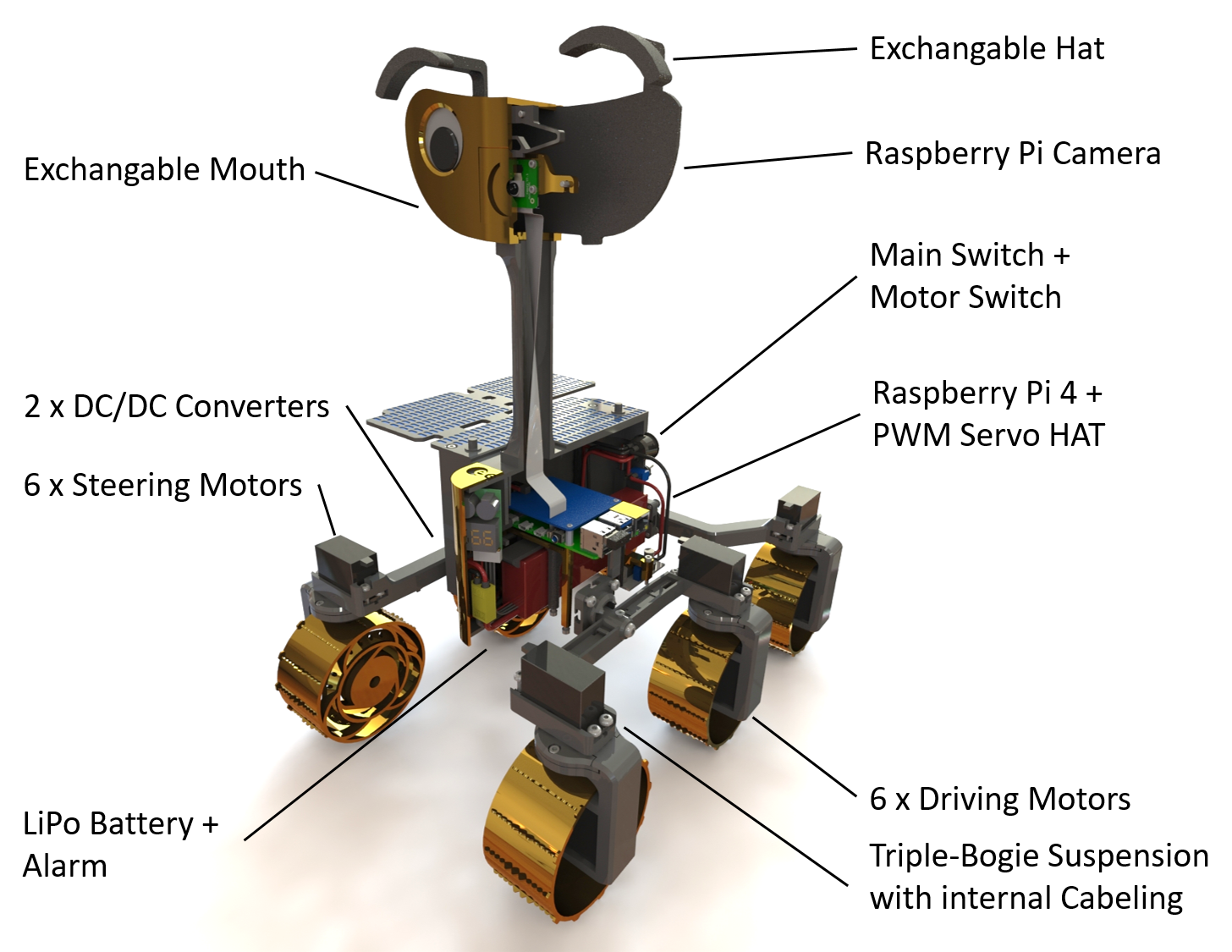
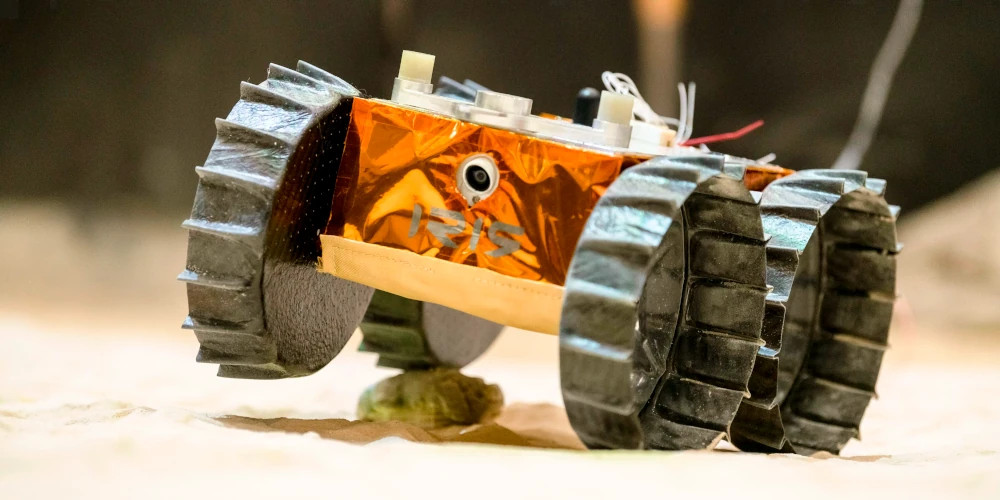
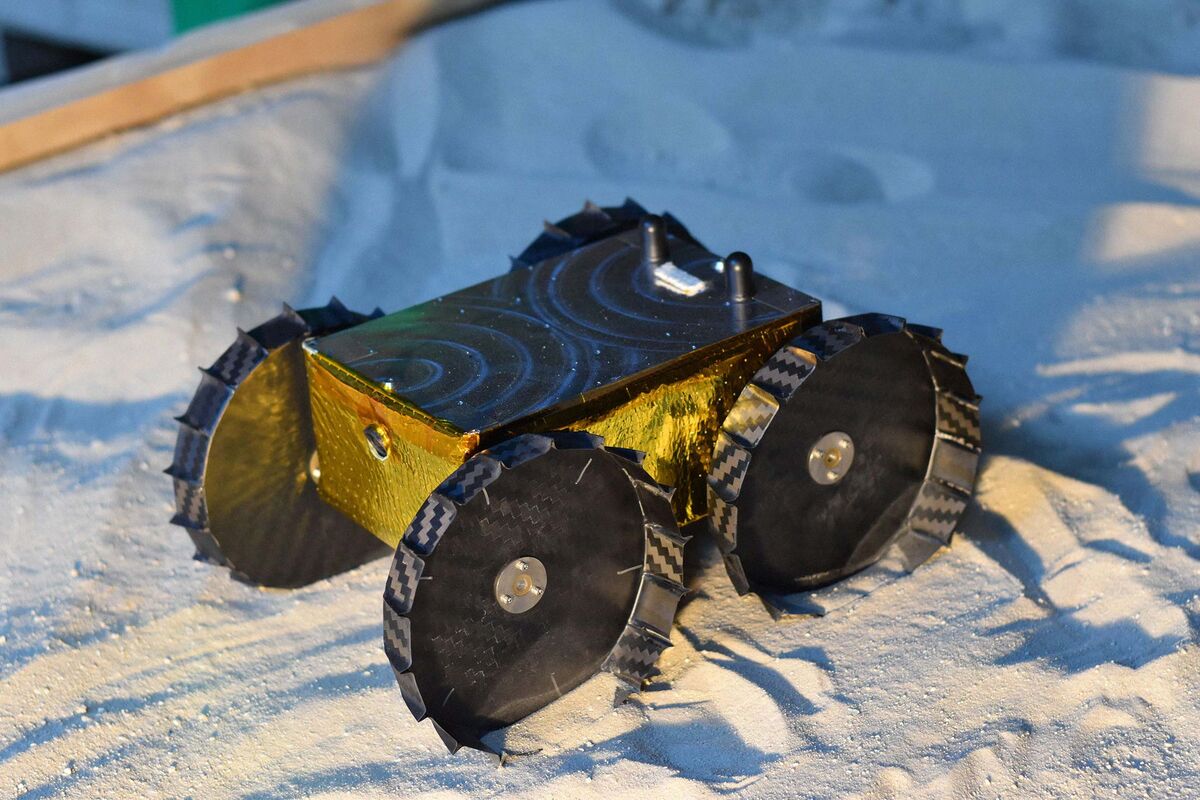
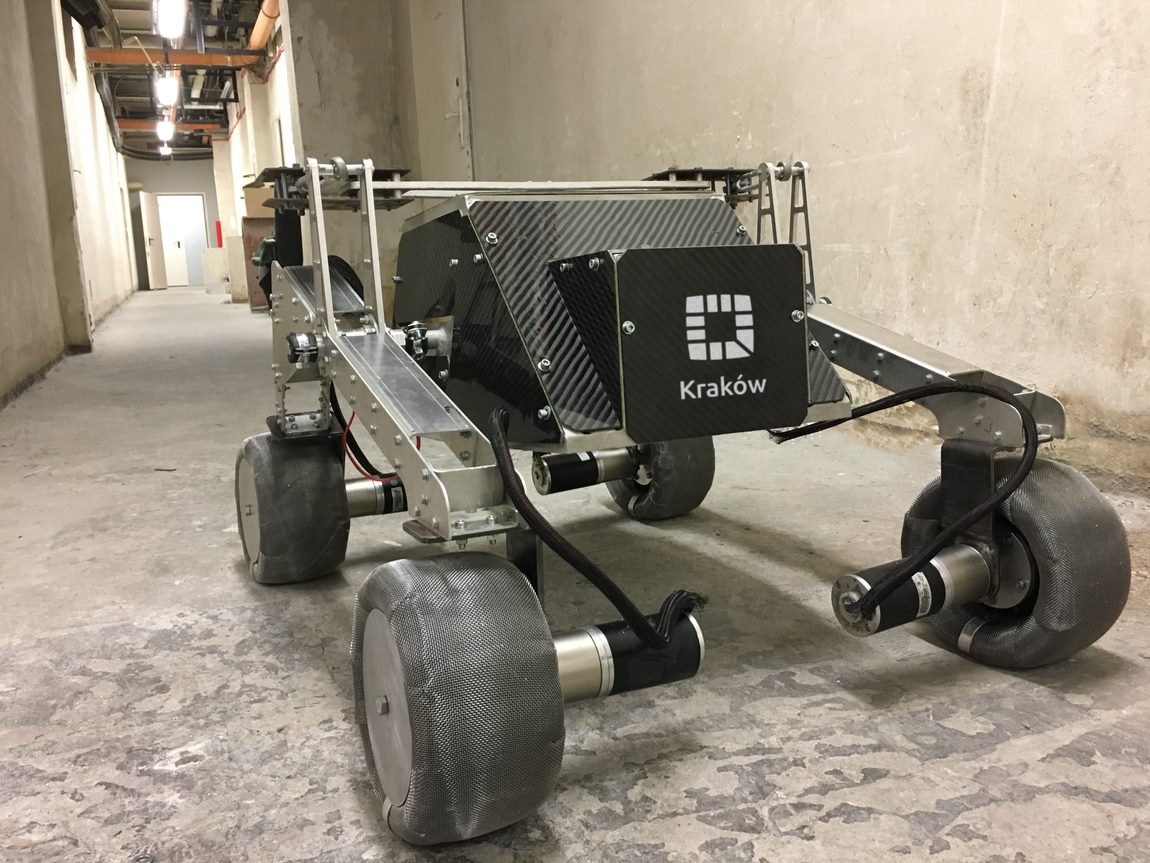
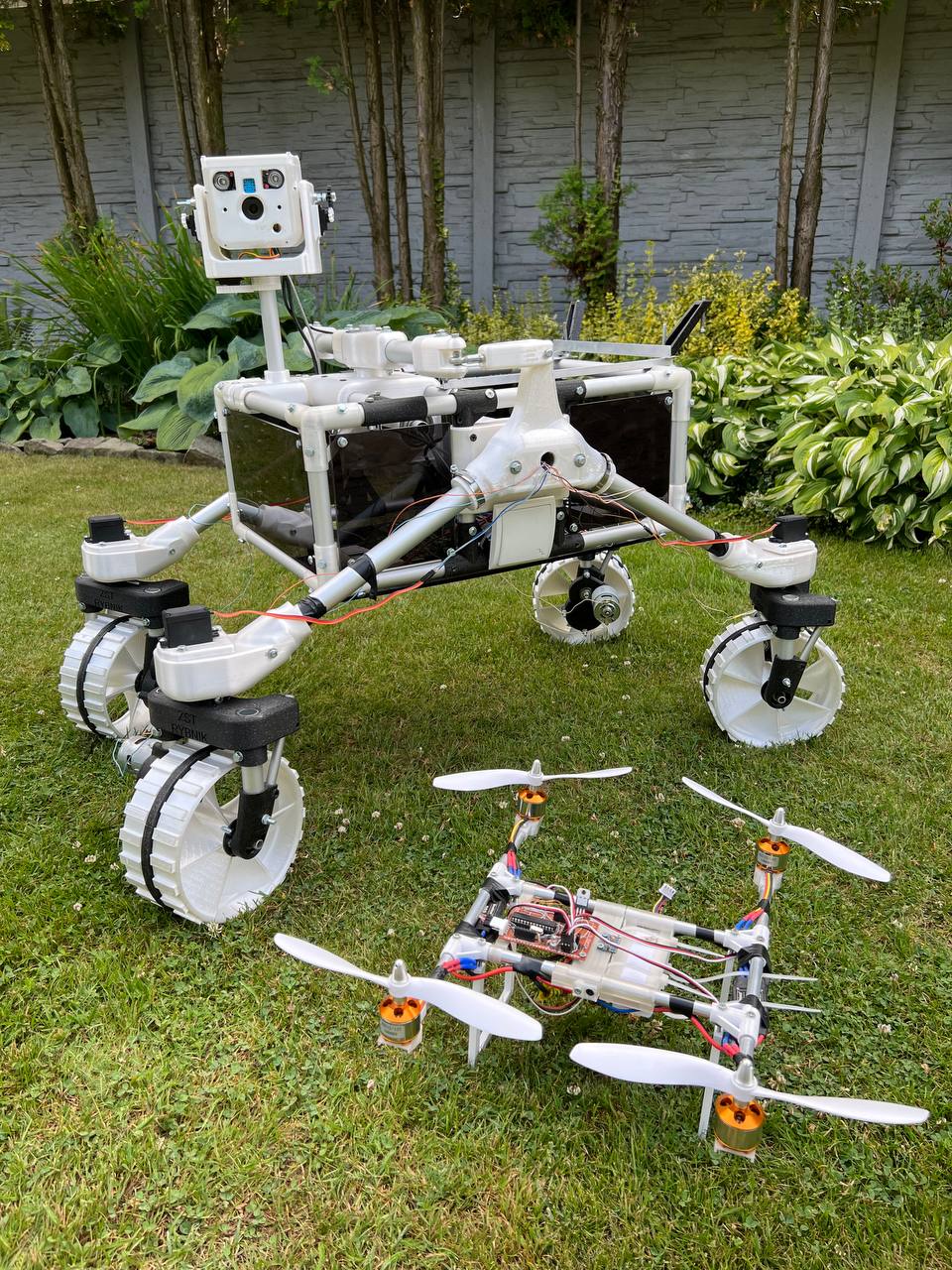
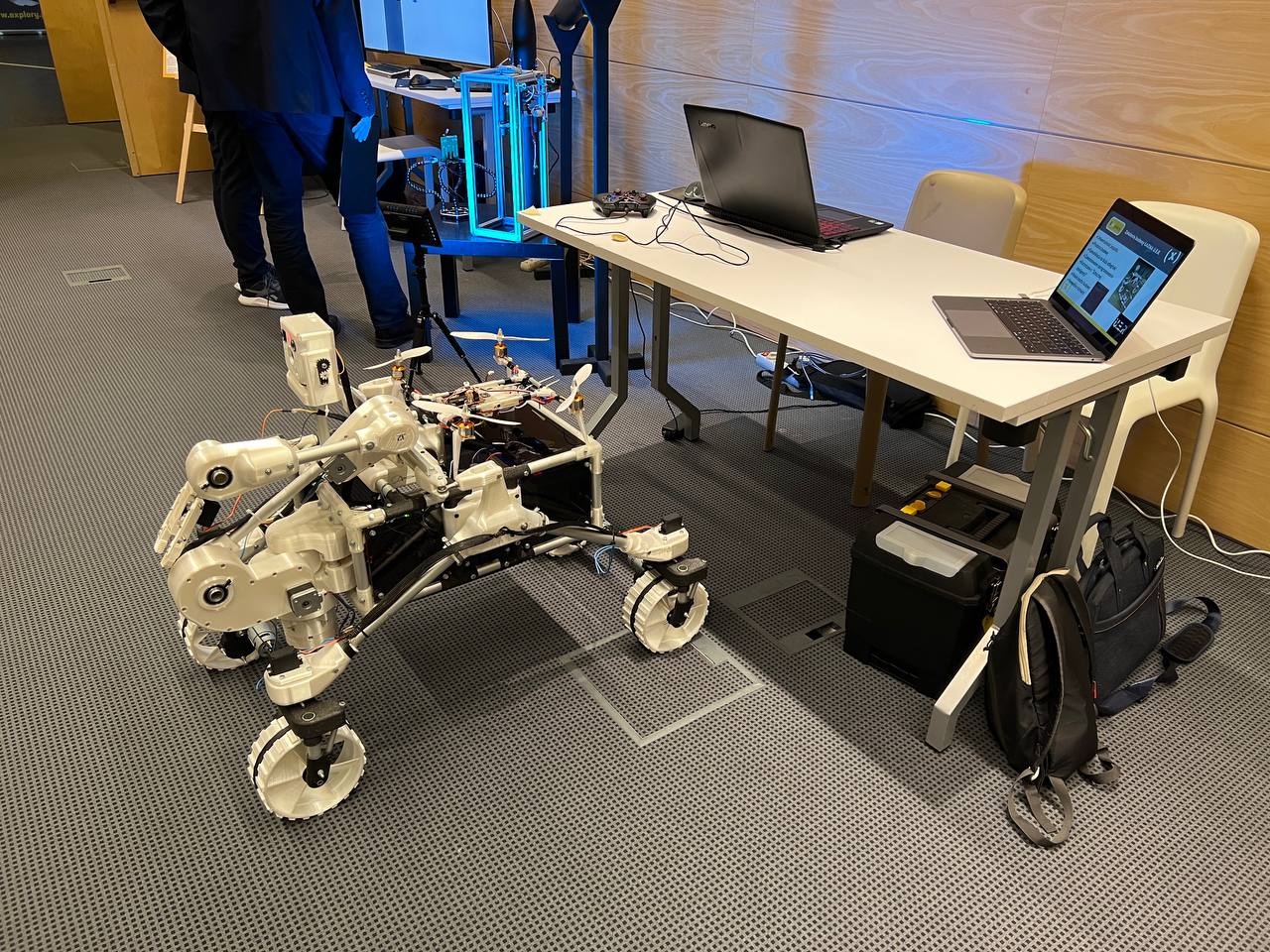
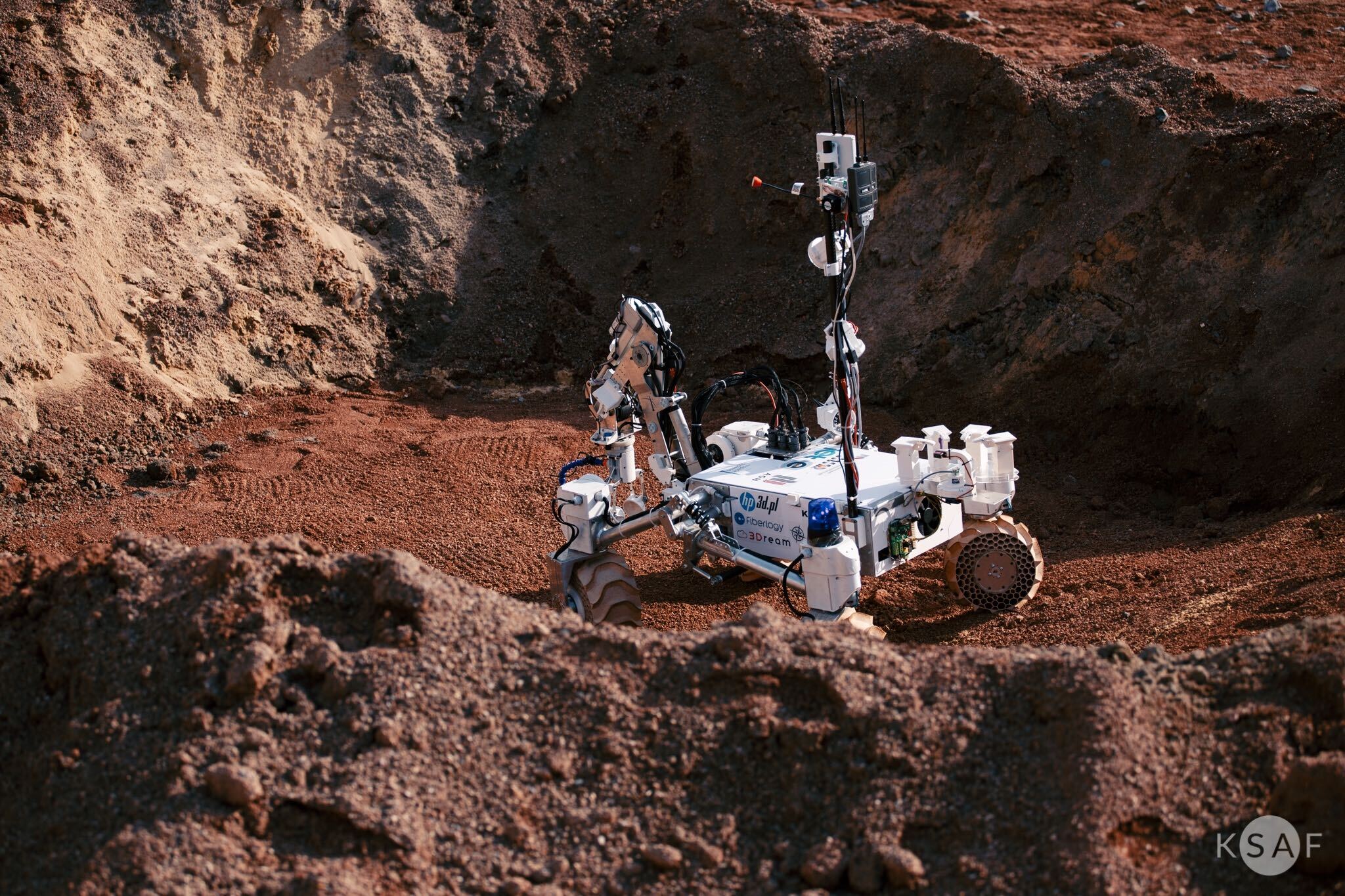
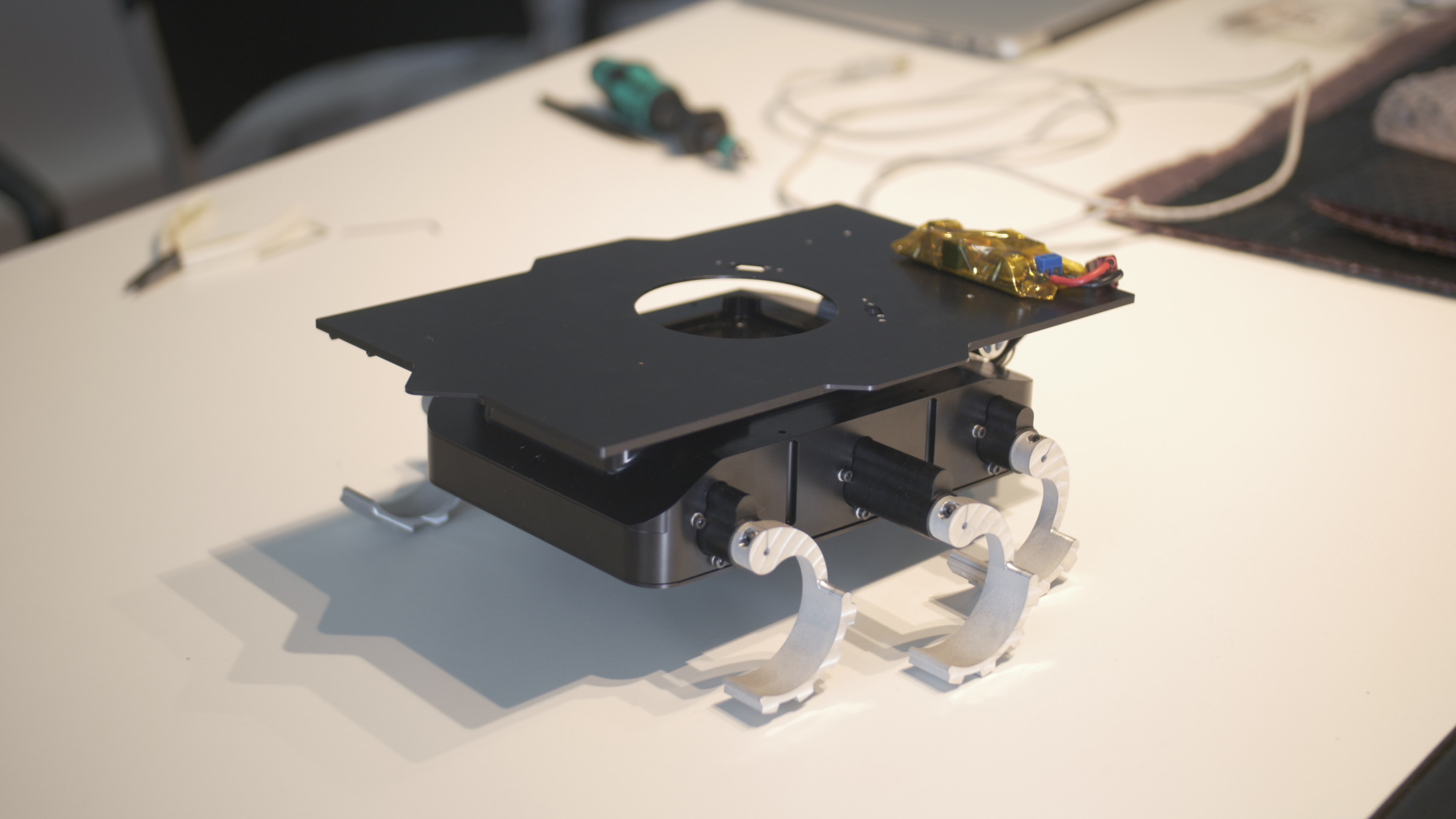
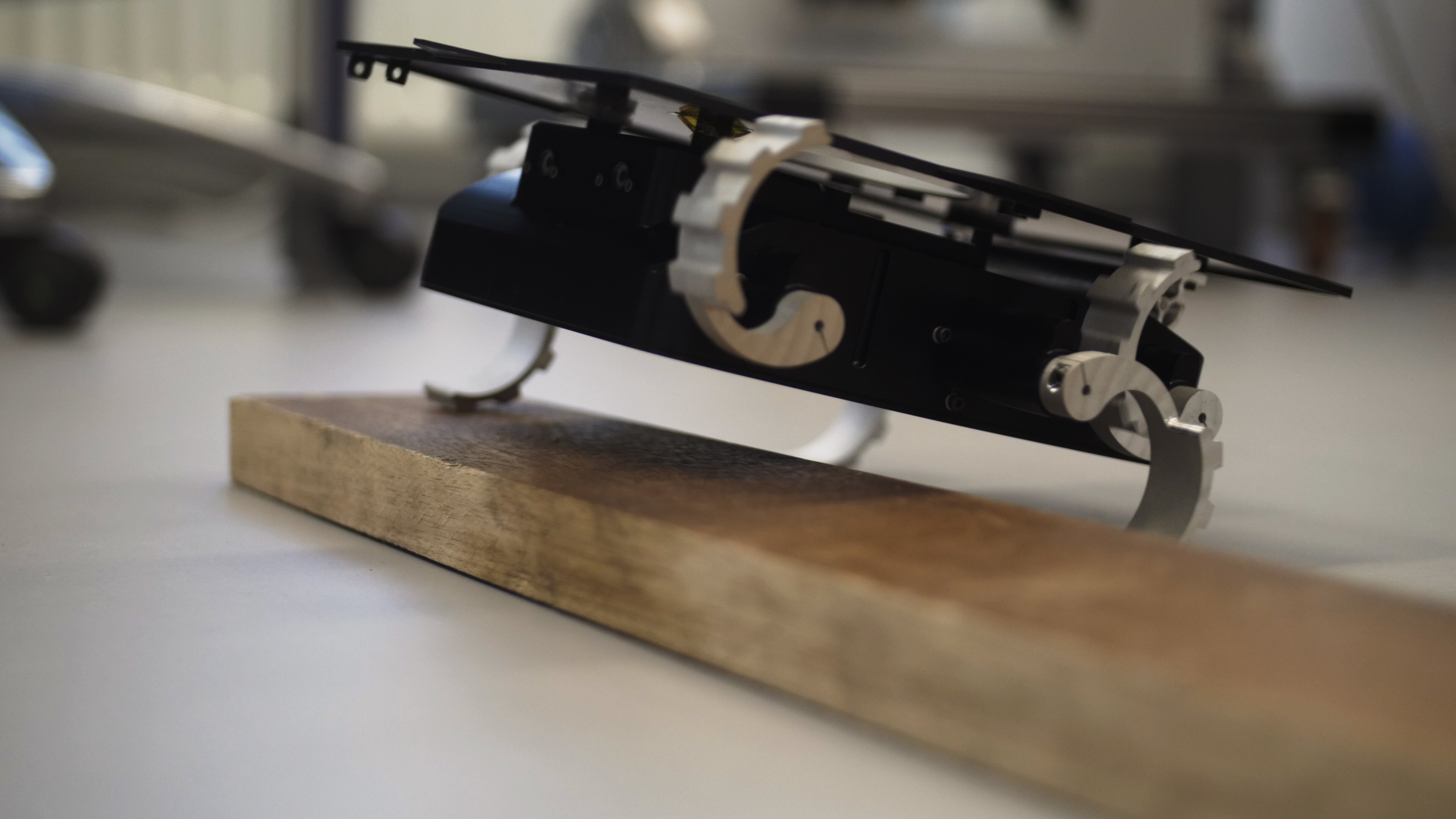
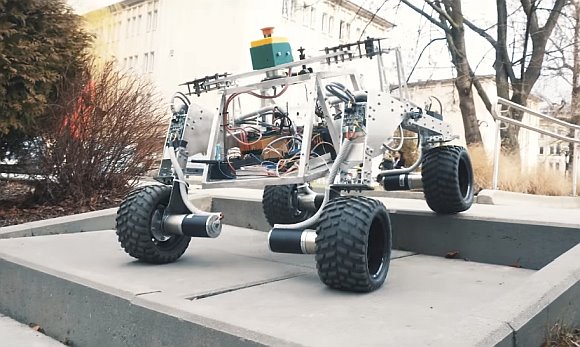
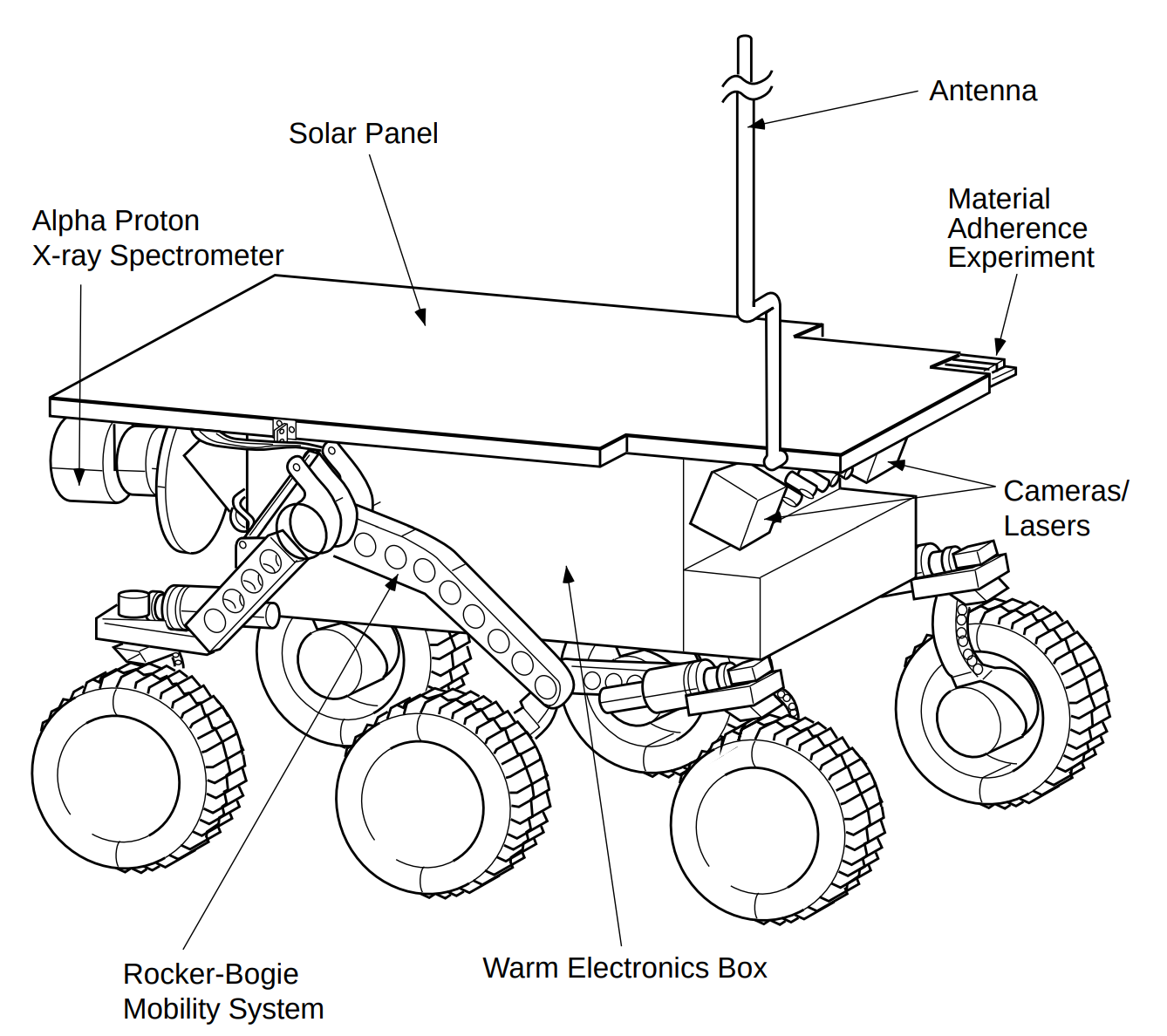
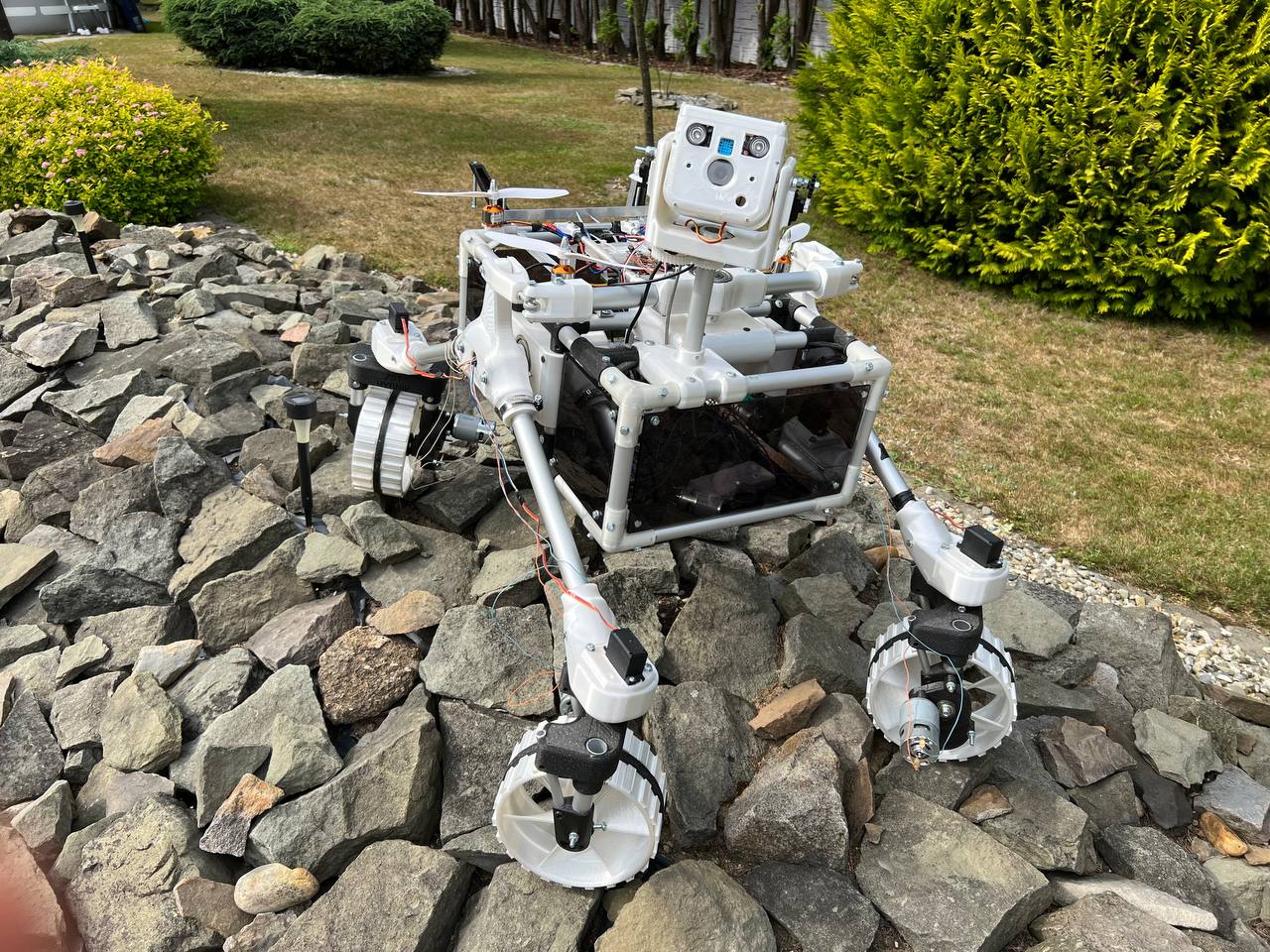
ExoMy is a 3D printed rover, designed as a low-cost robot platform for hobbyists, educators and researchers. All hardware and software is Open Source and was designed with ease-of-use and reliability in mind. The appearance of ExoMy can easily be customised, making it an interactive robotic platform for kids and adults alike.
The cost of ExoMy can range from 250€ to 500€. 3D-printing time is estimated at 2 weeks, and assembly time is estimated at 2 days.